-
概述
Zabbix的网络发现是指zabbix server通过配置好的规则,自动添加host,group,template
Zabbix的主动注册刚好和网络发现是相反的,功能基本一致。zabbix agent主动联系zabbix server,server自动添加host,group,template
以上两种方式都是发现host,添加host,而low-level discovery(低级自动发现)更加底层,用于发现item,trigger,graph等等。
2.MySQL多实例的低级自动发现
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 | (1)配置3307、3308的实例 [root@linux-node2 ~]# mkdir /data/{3307,3308} -p [root@linux-node2 ~]# chown -R mysql.mysql /data [root@linux-node2 ~]# cp /etc/my.cnf /etc/my3307.cnf [root@linux-node2 ~]# vim /etc/my3307.cnf [mysqld] datadir=/data/3307 socket=/data/3307/mysql.sock # Disabling symbolic-links is recommended to prevent assorted security risks symbolic-links=0 port=3307 # Settings user and group are ignored when systemd is used. # If you need to run mysqld under a different user or group, # customize your systemd unit file for mariadb according to the # instructions in http://fedoraproject.org/wiki/Systemd [mysqld_safe] log-error=/data/3307/mariadb.log pid-file=/data/3307/mariadb.pid # # include all files from the config directory # !includedir /etc/my.cnf.d [root@linux-node2 ~]# cp /etc/my3307.cnf /etc/my3308.cnf [root@linux-node2 ~]# vim /etc/my3308.cnf [mysqld] datadir=/data/3308 socket=/data/3308/mysql.sock # Disabling symbolic-links is recommended to prevent assorted security risks symbolic-links=0 port=3308 # Settings user and group are ignored when systemd is used. # If you need to run mysqld under a different user or group, # customize your systemd unit file for mariadb according to the # instructions in http://fedoraproject.org/wiki/Systemd [mysqld_safe] log-error=/data/3308/mariadb.log pid-file=/data/3308/mariadb.pid # # include all files from the config directory # !includedir /etc/my.cnf.d (2)初始化数据库 [root@linux-node2 ~]# mysql_install_db --user=mysql --defaults-file=/etc/my3307.cnf Installing MariaDB/MySQL system tables in '/data/3307' ... 171218 12:01:02 [Note] /usr/libexec/mysqld (mysqld 5.5.56-MariaDB) starting as process 4804 ... OK Filling help tables... 171218 12:01:02 [Note] /usr/libexec/mysqld (mysqld 5.5.56-MariaDB) starting as process 4813 ... OK To start mysqld at boot time you have to copy support-files/mysql.server to the right place for your system PLEASE REMEMBER TO SET A PASSWORD FOR THE MariaDB root USER ! To do so, start the server, then issue the following commands: '/usr/bin/mysqladmin' -u root password 'new-password' '/usr/bin/mysqladmin' -u root -h linux-node2 password 'new-password' Alternatively you can run: '/usr/bin/mysql_secure_installation' which will also give you the option of removing the test databases and anonymous user created by default. This is strongly recommended for production servers. See the MariaDB Knowledgebase at http://mariadb.com/kb or the MySQL manual for more instructions. You can start the MariaDB daemon with: cd '/usr' ; /usr/bin/mysqld_safe --datadir='/data/3307' You can test the MariaDB daemon with mysql-test-run.pl cd '/usr/mysql-test' ; perl mysql-test-run.pl Please report any problems at http://mariadb.org/jira The latest information about MariaDB is available at http://mariadb.org/. You can find additional information about the MySQL part at: http://dev.mysql.com Consider joining MariaDB's strong and vibrant community: https://mariadb.org/get-involved/ [root@linux-node2 ~]# mysqld_safe --defaults-file=/etc/my3307.cnf & [1] 4825 [root@linux-node2 ~]# 171218 12:01:53 mysqld_safe Logging to '/data/3307/mariadb.log'. 171218 12:01:53 mysqld_safe Starting mysqld daemon with databases from /data/3307 [root@linux-node2 ~]# mysql_install_db --user=mysql --defaults-file=/etc/my3308.cnf Installing MariaDB/MySQL system tables in '/data/3308' ... 171218 12:03:48 [Note] /usr/libexec/mysqld (mysqld 5.5.56-MariaDB) starting as process 5041 ... OK Filling help tables... 171218 12:03:48 [Note] /usr/libexec/mysqld (mysqld 5.5.56-MariaDB) starting as process 5049 ... OK To start mysqld at boot time you have to copy support-files/mysql.server to the right place for your system PLEASE REMEMBER TO SET A PASSWORD FOR THE MariaDB root USER ! To do so, start the server, then issue the following commands: '/usr/bin/mysqladmin' -u root password 'new-password' '/usr/bin/mysqladmin' -u root -h linux-node2 password 'new-password' Alternatively you can run: '/usr/bin/mysql_secure_installation' which will also give you the option of removing the test databases and anonymous user created by default. This is strongly recommended for production servers. See the MariaDB Knowledgebase at http://mariadb.com/kb or the MySQL manual for more instructions. You can start the MariaDB daemon with: cd '/usr' ; /usr/bin/mysqld_safe --datadir='/data/3308' You can test the MariaDB daemon with mysql-test-run.pl cd '/usr/mysql-test' ; perl mysql-test-run.pl Please report any problems at http://mariadb.org/jira The latest information about MariaDB is available at http://mariadb.org/. You can find additional information about the MySQL part at: http://dev.mysql.com Consider joining MariaDB's strong and vibrant community: https://mariadb.org/get-involved/ [root@linux-node2 ~]# mysqld_safe --defaults-file=/etc/my3308.cnf & [2] 5061 [root@linux-node2 ~]# 171218 12:03:56 mysqld_safe Logging to '/data/3308/mariadb.log'. 171218 12:03:56 mysqld_safe Starting mysqld daemon with databases from /data/3308 [root@linux-node2 ~]# netstat -tulnp Active Internet connections (only servers) Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:3307 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 4972/mysqld tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:3308 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 5207/mysqld tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 8237/nginx: master tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 866/sshd tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:25 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 2235/master tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:10050 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3263/zabbix_agentd tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:3306 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 4645/mysqld tcp6 0 0 :::22 :::* LISTEN 866/sshd tcp6 0 0 ::1:25 :::* LISTEN 2235/master tcp6 0 0 :::10050 :::* LISTEN 3263/zabbix_agentd [root@linux-node2 ~]# netstat -tulnp |grep mysql|awk -F "[ :]+" '{print $5}' 3307 3308 3306 (3)编写获取端口号的shell脚本 [root@linux-node2 scripts]# vim discovery_mysql.sh #!/bin/bash #mysql low-lever discovery res=`netstat -lntp|grep mysql |awk -F "[ :]+" '{print $5}'` port=($res) printf '{' printf '"data":[' for key in ${!port[@]} do if [[ "${#port[@]}" -gt 1 && "${key}" -ne "$((${#port[@]}-1))" ]];then printf '{' printf "\"{#MYSQLPORT}\":\"${port[${key}]}\"}," else [[ "${key}" -eq "((${#port[@]}-1))" ]] printf '{' printf "\"{#MYSQLPORT}\":\"${port[${key}]}\"}" fi done printf ']' printf '}' [root@linux-node2 scripts]# sh discovery_mysql.sh |python -m json.tool #采用json格式显示 { "data": [ { "{#MYSQLPORT}": "3307" }, { "{#MYSQLPORT}": "3308" }, { "{#MYSQLPORT}": "3306" } ] } [root@linux-node2 zabbix_agentd.d]# vim discovery_mysql.conf #编辑自定义key UserParameter=discovery_mysql,/bin/bash /etc/zabbix/zabbix_agentd.d/scripts/discovery_mysql.sh [root@linux-node1 ~]# zabbix_get -s linux-node2 -k discovery_mysql #测试server端获取数据 (Not all processes could be identified, non-owned process info will not be shown, you would have to be root to see it all.) {"data":[]} #这里报错是因为netstat -tulnp的参数-p在执行时需要root的权限,这里使用suid的方式进行授权 [root@linux-node2 ~]# chmod u+s `which netstat` [root@linux-node2 ~]# ll `which netstat` -rwsr-xr-x. 1 root root 155000 8月 3 17:17 /usr/bin/netstat [root@linux-node1 ~]# zabbix_get -s linux-node2 -k discovery_mysql {"data":[{"{#MYSQLPORT}":"3307"},{"{#MYSQLPORT}":"3308"},{"{#MYSQLPORT}":"3306"}]} (4)编辑自定义key,获取每个端口的状态数据 [root@linux-node2 zabbix_agentd.d]# cat userparameter_mysql.conf UserParameter=mysql.status[*],echo "show global status where Variable_name='$2';" | HOME=/var/lib/zabbix mysql -uroot -p123456 -h 127.0.0.1 -P $1 -N | awk '{print $$2}' 修改不同端口的mysql密码: [root@linux-node2 zabbix_agentd.d]# mysqladmin -h 127.0.0.1 -uroot password '123456' -P3306 [root@linux-node2 zabbix_agentd.d]# mysqladmin -h 127.0.0.1 -uroot password '123456' -P3307 [root@linux-node2 zabbix_agentd.d]# mysqladmin -h 127.0.0.1 -uroot password '123456' -P3308 测试是否正常 [root@linux-node2 zabbix_agentd.d]# mysql -uroot -p123456 -h 127.0.0.1 -P3306 -e "use mysql;show GLOBAL VARIABLES like 'port';" +---------------+-------+ | Variable_name | Value | +---------------+-------+ | port | 3306 | +---------------+-------+ [root@linux-node2 zabbix_agentd.d]# mysql -uroot -p123456 -h 127.0.0.1 -P3307 -e "use mysql;show GLOBAL VARIABLES like 'port';" +---------------+-------+ | Variable_name | Value | +---------------+-------+ | port | 3307 | +---------------+-------+ [root@linux-node2 zabbix_agentd.d]# mysql -uroot -p123456 -h 127.0.0.1 -P3308 -e "use mysql;show GLOBAL VARIABLES like 'port';" +---------------+-------+ | Variable_name | Value | +---------------+-------+ | port | 3308 | +---------------+-------+ zabbix_get测试是否能正常获取数据: [root@linux-node1 ~]# zabbix_get -s linux-node2 -k mysql.status[3306,Bytes_sent] 1808 |
3.创建发现规则
这里直接在linux-node2上进行创建
| 1 | "Configuration" --> "Host" --> "linux-node2" --> "Discovery" --> "Create discovery rule" --> "Add" |
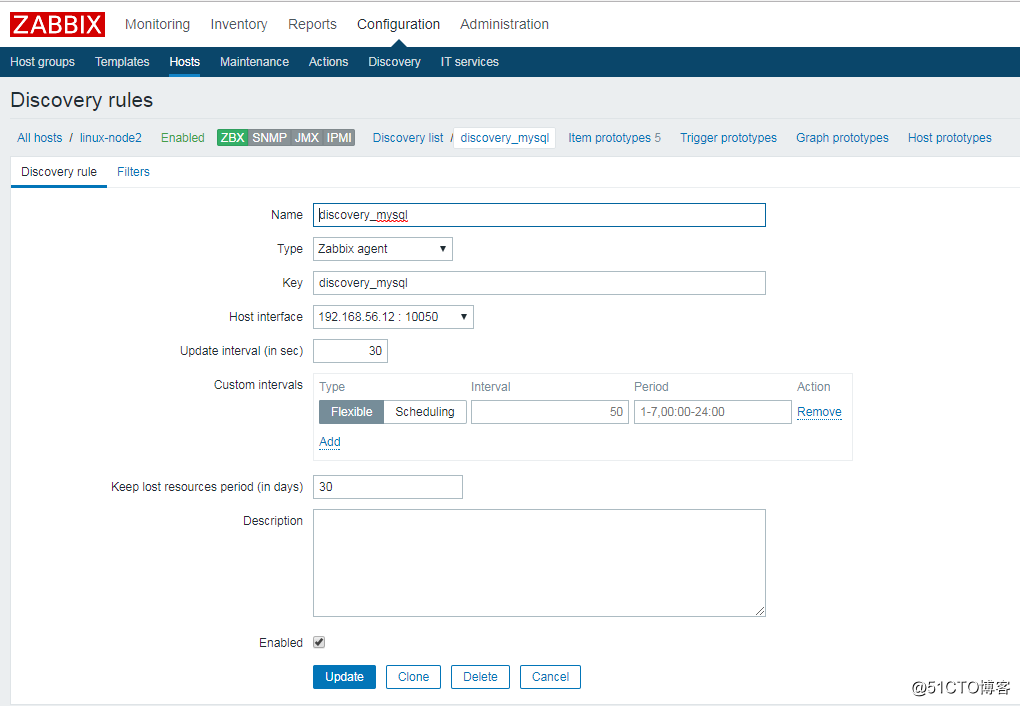
创建 Item prototypes,其实就是一个创建一个 item
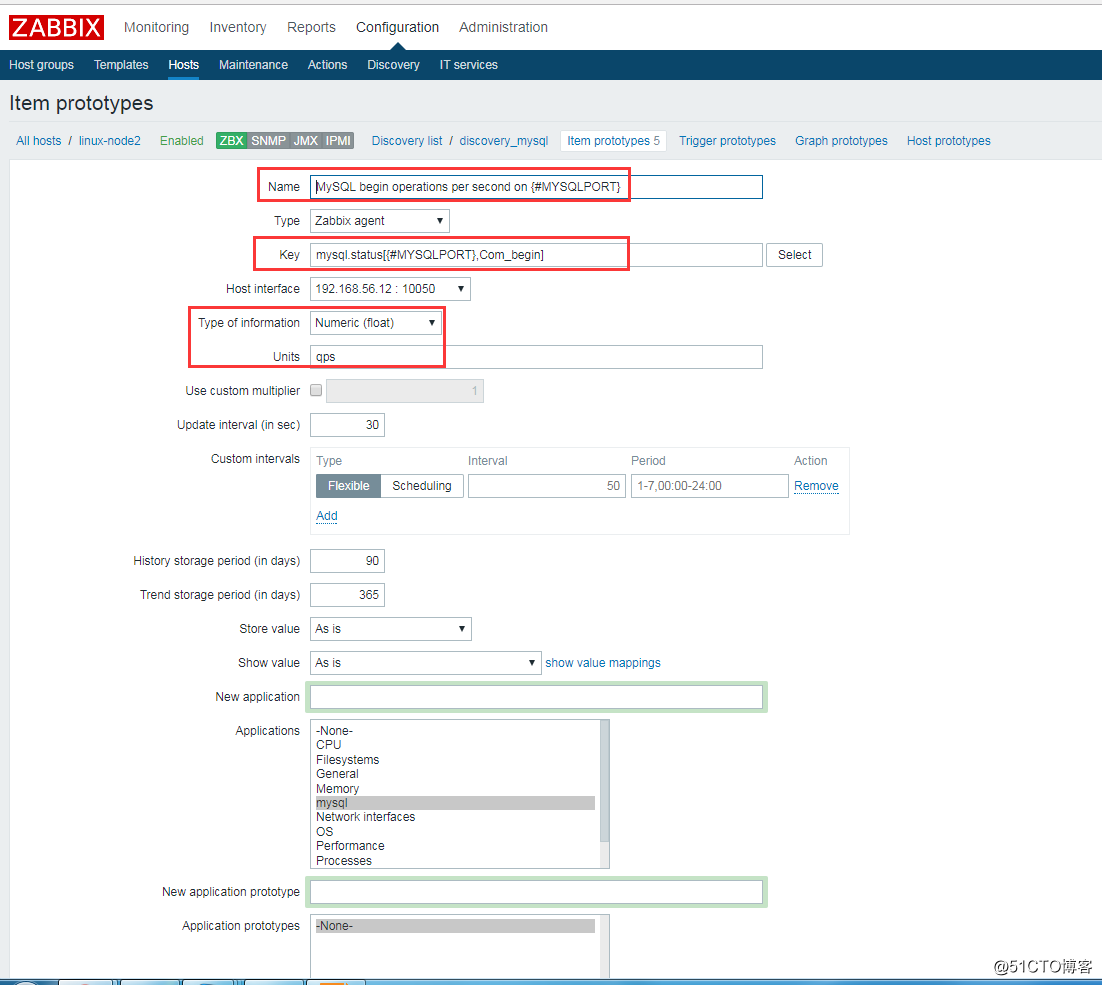
Item prototypes (0)>>create Item prototypes,按照官方模板来配置。这里配5个展示
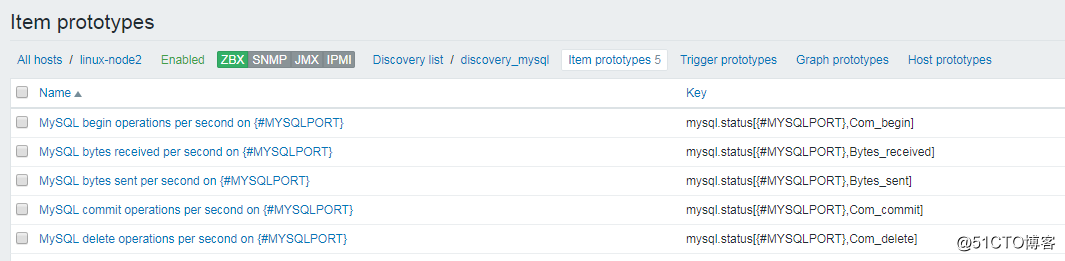
再查看Host中的item项,会多出以下监控项:
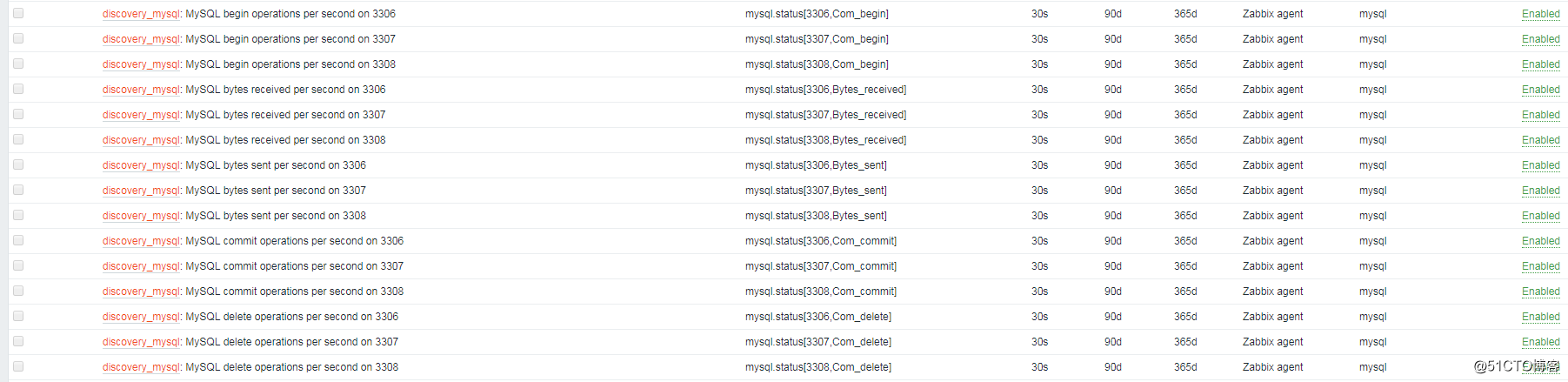
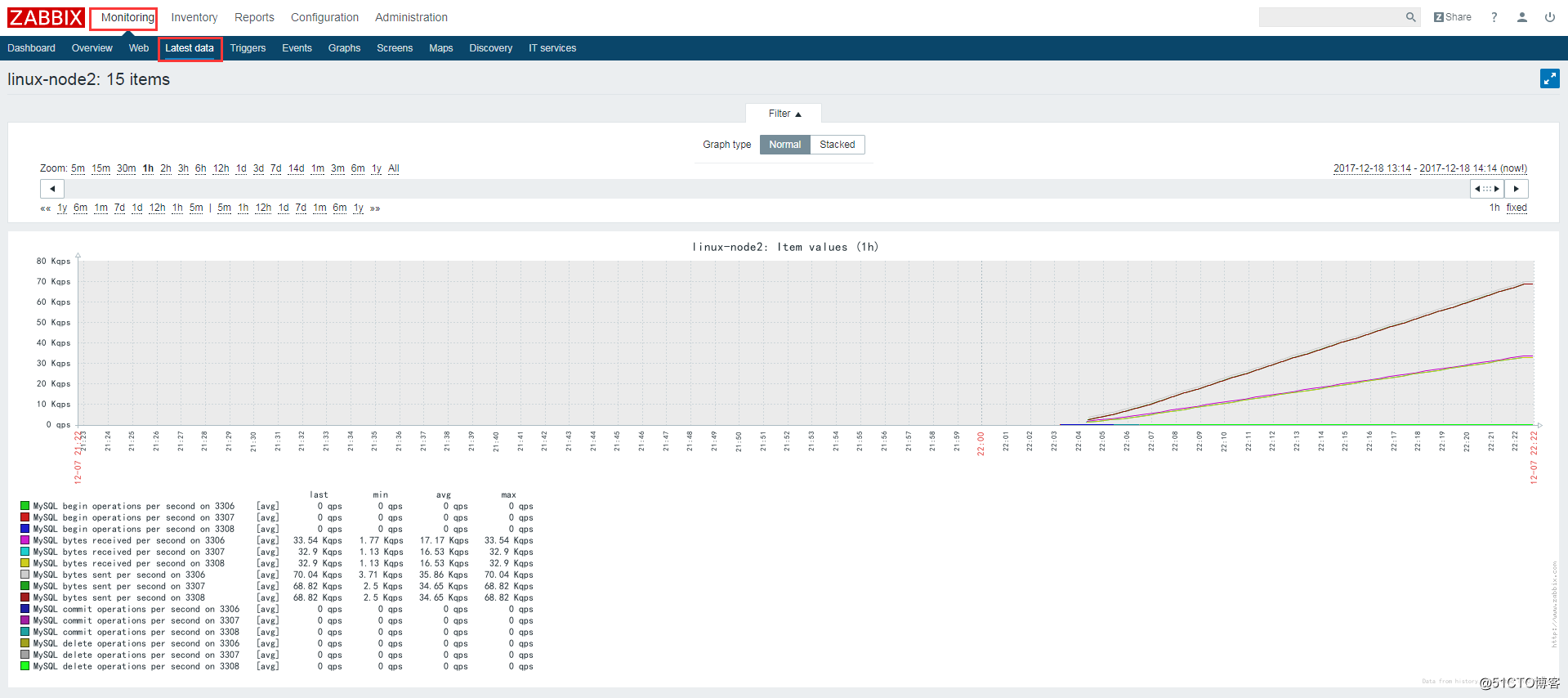
查看监控最新数据图表,即可看到3306、3307、3308的数据库状态信息: